Have you ever wondered how your body breaks down glycogen to release energy? Well, let me tell you, my friend, that it's all about glycogenolysis, a complex process that takes place in different parts of your body. Let's dive into the world of glycogenolysis and discover how it works.
Glycogenolysis in Muscles and Liver
Muscles
When you exercise or engage in any physical activity, your muscles need energy to perform. They get this energy from glycogen, a stored form of glucose, which they break down through the process of glycogenolysis. In muscles, this process happens in the cytosol, a compartment within the cell.

Liver
Your liver also stores glycogen, but it serves a different purpose. When your blood glucose levels drop, the liver breaks down stored glycogen and releases glucose into the bloodstream to raise your blood sugar levels back to normal. This is why the process of glycogenolysis in the liver is so important for maintaining your body's glucose homeostasis. In the liver, glycogenolysis takes place in the cytosol and the endoplasmic reticulum.
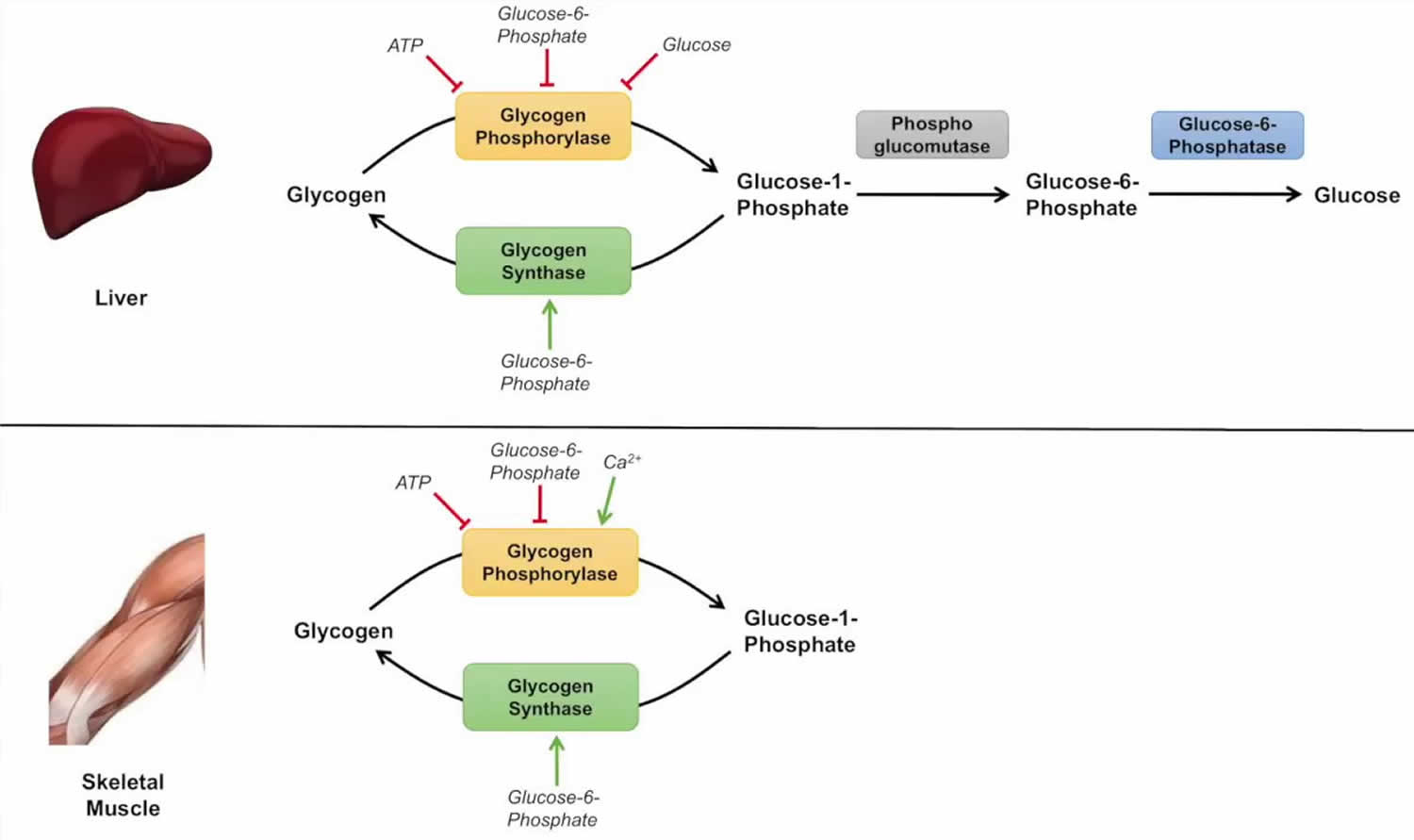
The Glycogenolysis Pathway
Now that you know where glycogenolysis takes place, let's talk about the steps involved in the process.
Step 1: Phosphorylation
Glycogenolysis begins with the phosphorylation of glycogen by an enzyme called glycogen phosphorylase. This enzyme adds a phosphate molecule to the glycogen molecule, breaking it down into glucose-1-phosphate.
Step 2: Isomerization
The glucose-1-phosphate molecule is then converted into glucose-6-phosphate through the process of isomerization. This step is catalyzed by an enzyme called phosphoglucomutase.
Step 3: Debranching Enzyme
The debranching enzyme then comes into play and helps break down the glycogen molecule further. It removes a branch of glucose molecules from the glycogen chain and converts them into glucose-1-phosphate.
Step 4: Phosphorylase
After the debranching enzyme has done its work, glycogen phosphorylase takes over again, breaking down the remaining glycogen chains into glucose-1-phosphate.
Step 5: Conversion to Glucose-6-Phosphate
Finally, the glucose-1-phosphate molecules are converted into glucose-6-phosphate, which can then be used for energy production or stored for later use.
Tips for Maximizing Glycogenolysis
Now that you know how glycogenolysis works, let's talk about some tips for maximizing the process to get the most out of your workouts.
Tip 1: Eat a High-Carb Diet
Glycogen stores are replenished through the consumption of carbohydrates, so it's important to eat a diet that's high in complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. This will help ensure that you have adequate glycogen stores to fuel your workouts.
Tip 2: Time Your Carbs
When you eat carbs can also impact your glycogen stores. Eating carbs before and after your workouts can help ensure that your glycogen stores are full and ready to go when you need them.
Tip 3: Supplement with Creatine
Creatine is a popular supplement that can help increase your body's production of ATP, the molecule responsible for providing energy to your muscles during exercise. By supplementing with creatine, you can help maximize your body's glycogenolysis process and improve your workout performance.
Conclusion
Glycogenolysis is a complex process that takes place in different parts of your body, including your muscles and liver. By understanding how this process works, you can maximize your glycogen stores and get the most out of your workouts. Remember to eat a high-carb diet, time your carbs, and consider supplementing with creatine to maximize your glycogenolysis and take your workouts to the next level!
Find more articles about Where Does Glycogenolysis Take Place